Role of Intumescent Coatings in Building Design
An Architectural Perspective
Fire safety is a cornerstone of modern architecture, necessitating meticulous planning and the integration of advanced technologies to ensure occupant safety and structural integrity. Among the many fire protection solutions available, intumescent coatings have emerged as a critical component in building design. This article delves into the role of intumescent coatings in architectural practice, highlighting their functionality, application, and relevance, with specific reference to examples from Australia.
What Are Intumescent Coatings?
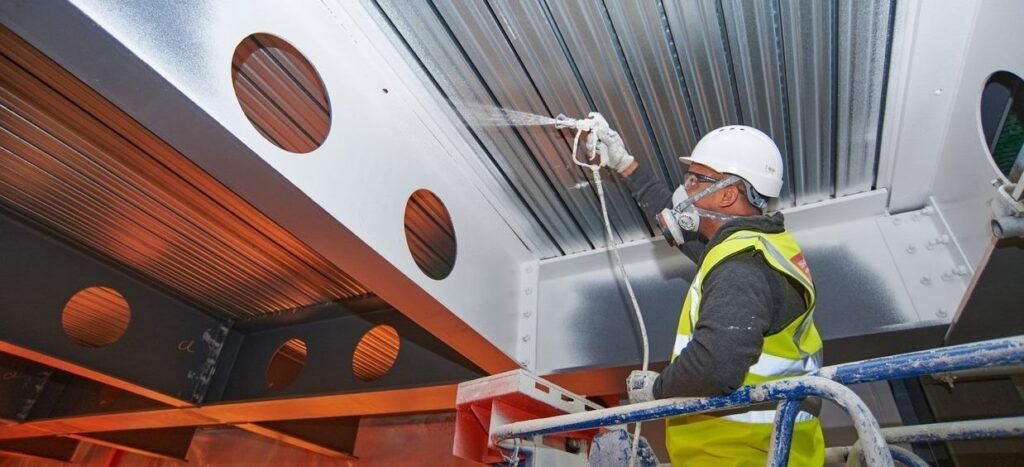
Intumescent coatings are a type of passive fire protection material designed to safeguard building elements during a fire. When exposed to high temperatures, these coatings undergo a chemical reaction, expanding to form a thick, insulating char layer. This char slows the heat transfer to the underlying material, thereby extending the time before the material reaches its critical failure temperature.
These coatings are most commonly applied to steel structures, though they can also be used on timber, concrete, and other substrates. By preserving the structural integrity of materials during a fire, intumescent coatings provide occupants with crucial additional evacuation time and help minimise property damage.
How Do Intumescent Coatings Work?
The mechanism of intumescent coatings is based on a series of thermal reactions:
- Dehydration: The coating releases water vapour, which cools the surface temporarily.
- Char Formation: Organic compounds within the coating react to form a carbonaceous char.
- Foaming: Blowing agents in the coating expand, creating a dense foam that insulates the substrate from heat.
These reactions occur in sequence as the temperature rises, effectively delaying the temperature increase in the protected material. The thickness and composition of the coating can be tailored to meet specific fire resistance ratings, such as 30, 60, or 120 minutes.
Applications in Building Design
Intumescent coatings are versatile and can be employed in various settings. Their primary applications include:
- Structural Steel Protection: Steel, a widely used construction material, begins to lose its strength at temperatures above 500°C. Intumescent coatings can delay this process, ensuring that steel structures maintain their load-bearing capacity during a fire.
- Timber Preservation: As timber gains popularity in sustainable building practices, fire safety becomes paramount. Intumescent coatings enhance the fire resistance of exposed timber elements without compromising their aesthetic appeal.
- Concrete Structures: While concrete is inherently fire-resistant, intumescent coatings can provide additional protection, particularly in high-risk areas.
- Façade Systems: Modern architecture often features complex façade designs incorporating lightweight and combustible materials. Intumescent coatings can be used to mitigate fire risks in such systems.
Advantages
Intumescent coatings offer several advantages over traditional fire protection methods:
- Aesthetic Flexibility: Unlike bulky fireproof cladding or sprayed coatings, intumescent coatings can be applied as a thin, paint-like layer, preserving the visual appeal of architectural elements.
- Lightweight Solution: They add minimal weight to structures, making them ideal for retrofitting and modern high-rise designs.
- Customisation: Coatings can be customised to achieve specific fire ratings and finishes, including colours and textures.
- Ease of Application: Intumescent coatings are relatively straightforward to apply, using spray, roller, or brush techniques.
Challenges and Considerations
While intumescent coatings offer numerous benefits, their application comes with certain challenges:
- Cost: High-quality intumescent coatings can be more expensive than traditional fireproofing methods. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
- Application Expertise: Proper application is critical to achieving the desired fire resistance. Trained professionals must apply the coatings to ensure uniform thickness and adherence.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors such as humidity, temperature, and substrate condition can affect the performance of intumescent coatings.
- Maintenance: Periodic inspections are necessary to ensure the coatings remain intact and effective over time.
Future Directions for Intumescent Coating Technology
As architectural trends evolve, the demand for innovative fire protection solutions will continue to grow. Intumescent coatings are likely to play a pivotal role in:
- Sustainable Construction: With the increasing use of timber and lightweight materials, intumescent coatings will be integral to achieving fire-safe yet eco-friendly designs.
- Retrofitting Heritage Buildings: These coatings offer a non-invasive way to upgrade the fire resistance of historic structures without altering their appearance.
- Integration with Smart Systems: Combining intumescent coatings with digital technologies will enhance fire monitoring and management capabilities.
Australian Perspective
In Australia, fire protection measures must comply with the National Construction Code (NCC) and relevant Australian Standards. Intumescent coatings are typically assessed under standards such as AS 1530.4 (Methods for Fire Tests on Building Materials, Components and Structures) and AS 4100 (Steel Structures).
The coatings must be tested and certified to meet the required Fire Resistance Levels (FRLs), expressed as a combination of structural adequacy, integrity, and insulation (e.g., 120/120/120).
Australian Examples – Intumescent Coatings in Practice
- Barangaroo International Towers, Sydney Barangaroo is a landmark development in Sydney, showcasing modern, sustainable architecture. The project involved extensive use of steel in its design. To meet stringent fire safety requirements, intumescent coatings were applied to the structural steel elements, ensuring compliance with Australian standards while maintaining the sleek aesthetic of the design.
- Melbourne Skyrail Project The Skyrail project, part of the Level Crossing Removal Programme, features elevated railways supported by concrete and steel structures. Intumescent coatings were used to protect these critical structural elements from fire risks, providing durability and long-term fire resistance in a high-traffic public infrastructure setting.
- Green Square Library, Sydney This award-winning public building incorporates exposed timber in its design. Intumescent coatings were applied to the timber elements to meet fire safety regulations while preserving the natural beauty of the material. The result is a visually striking yet safe architectural space.
Australia Leading the World
Intumescent coating blends safety, functionality, and aesthetics, making them an invaluable tool in modern architectural practice. Their ability to provide passive fire protection while accommodating diverse design aspirations aligns perfectly with the goals of contemporary architecture.
In Australia, where stringent fire safety regulations and a diverse range of building projects demand robust solutions, intumescent coatings have proven their worth. From iconic commercial developments like Barangaroo to innovative public infrastructure projects such as the Skyrail, these coatings are shaping the future of fire-safe, sustainable design. As technology advances, their role in architecture will undoubtedly expand, reinforcing the importance of integrating fire safety seamlessly into the fabric of building design.